Introduction
First, I would like to draw your attention that there is a huge difference between the diagnosis called Ovarian Cyst and a completely different disease called Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), the later was explained in detail in a different information leaflet. Ovarian cysts are usually solitary or few cysts, affecting a single ovary or both ovaries in rare cases.
Functional ovarian cysts
These are the commonest type of ovarian cysts. They usually disappear spontaneously within 3-4 months. The commonest type is the one producing the early pregnancy hormone. The second commonest subtype is a cyst developing from the growing ovulation follicle (Follicular cyst), this may be seen in temporary hormone disturbance as seen in periods of anxiety and disturbed sleep or rapid change of bodyweight, but when recurrent this type of cysts may be a hint to reduced ovarian reserve.
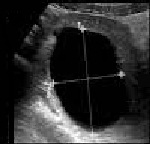
There is another subtype of functional cysts called the corpus luteum cyst which results after the normal process of ovulation, they usually disappear within two weeks and are common to give symptoms similar to the beginning of pregnancy.
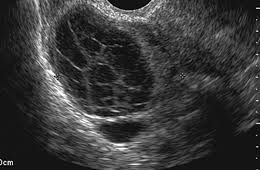
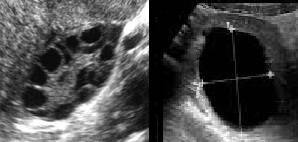
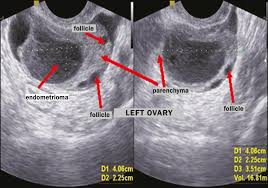
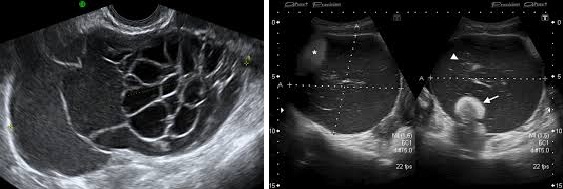
Benign ovarian tumor cysts
These are cysts which would not disappear without surgery. But since they are benign, one may often plan surgery on a date at patient’s convenience. The most common type is the Dermoid Cyst which is usually a solitary cyst growing in a single ovary which usually causes no symptoms until it reaches a considerable size to cause some pelvic discomfort. It has a characteristic shape on ultrasound examination. The second subtype is the Endometriosis Chocolate cyst which also has a characteristic appearance on ultrasound examination and is commonly associated with pelvic pain.
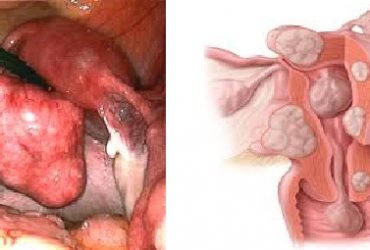
Malignant ovarian tumors
These are the least common but obviously most serious types. They usually affect older ages but are occasionally seen in young women and even in young children. They are rapid growing, usually bilateral masses which may be partly solid, containing areas of bleeding.
They usually present with colicky abdominal pain, bowel motion disturbances, abdominal distension, as well as loss of weight and poor appetite. They may be associated with symptoms related to spread of the tumor to other body organs.
My Best Wishes